Redirect Chains: How Do They Affect SEO and How to Fix it?
Setting up proper redirects while going to content updates or website migration is an important website maintenance step. However, many times, website owners or development teams overlook the importance of correct redirects.
They may intentionally or unintentionally create redirect chains that can negatively affect the website’s performance and SEO. While most people may not consider redirects as a technical SEO issue, there’s much more going on behind the scenes.
In this article, we’ll explain what redirect chains are and how they are created, and how to find redirect chains. So, let’s get started:
What is a Redirect Chain?
While visiting a page, have you ever experienced that you’ve clicked on a URL and it goes through multiple rounds of redirects to reach the final destination URL?
Well, that’s what a redirect chain is.
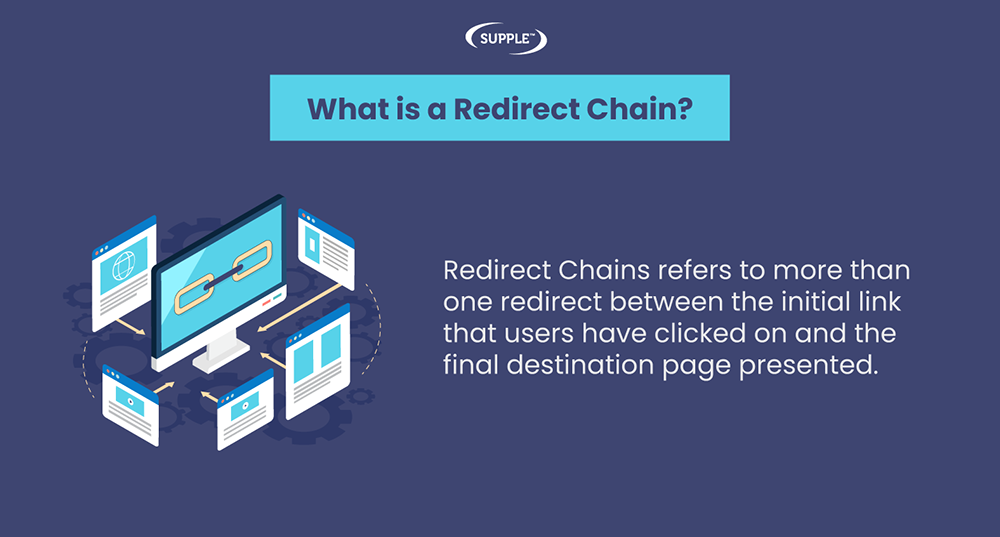
Redirect Chains refers to more than one redirect between the initial link that users have clicked on and the final destination page presented.
It’s a series of HTTP redirects that occur when users or search engine bots request a webpage that no longer exists or has been moved.
Redirects are an important on-page SEO factor. A redirect chain becomes active when a website redirects a page to another page, which also is redirected to another page, and so on until the user reaches the final page.
For instance, let’s imagine you click on Page1 from search results pages or from another web page to access its content but are redirected to Page2, Page3, or PageN.
Usually, the server locates the page and presents it to you. But in the redirect chain, the server will send you to a third, fourth, or nth number of page where the initial page has been moved permanently. This subsequent redirection of URL requests is called a redirect chain.
Having a single redirect from a URL is fine and does not impact much on the user experience and search rankings. However, a redirect chain can cause several problems including slower page load times that result in user frustration.
Since each redirect in the chain adds an additional HTTP request, it increases the time for a server to load the page and its content. Further, it signals poor website maintenance to search engines and affects the ranking in Search Engine Result Pages (SERP).
Why Redirects are Used?
Website redirects are typically used for a few reasons as listed below:
Direct Users to Main Page
There are seemingly wide variations in how users search a website and small changes such as HTTP or HTTPS and WWW vs non-WWW can drastically impact the final destination. A redirect ensures that the users land on the right website regardless of what they have entered.
For instance, if a user has entered “http://www.yourdomain.com”, a 301 redirect will ensure the users automatically see the “https://yourdomain.com”
Content Updates & Website Maintenance
When website owners want to move or update their content to a new location, they often use a 301 redirect. Doing so ensures that the users can still access the content even if the URL is changed and keep the SEO level the same as the initial page.
Also, since changing backlinks from the other side isn’t possible, you’d have to contact the site owner and ask them to make the necessary changes. However, it’s often quicker to redirect the initial backlink as the website grows and content changes.
The only catch is the number of redirects between the initial link and the destination page can increase dramatically, creating a redirect chain.
Multiple Domains and Website Restructuring
Multiple similar domains or URLs can lead to confusion and duplicate content issues that are solved using redirects. Also, when restructuring or reorganising a website, it's possible some URL structures need change in specifics.
For example, “http://yourdomain.com/products” is redirected to “https://yourdomain.com/product” as it lacks a secure HTTPS connection. However, there’s another issue of trailing slash after the “products”, which is again redirected to “https://yourdomain.com/products/”
This creates a two-step chain due to minor changes in the URL structure. But when performed at scale while restructuring the site, redirects can easily get out of hand.
Keep the SEO and Traffic Levels Intact from Old Site
Due to some reasons, you may decide to move your established website with a certain SEO and traffic level to another domain. However, you don’t want to lose all this traffic and the SEO work your team has put into the older site or URL.
To save all this hard work, you can take the route of 301 redirects to direct all the traffic from the old site to the new one. Doing so ensures that your SEO and traffic to the new website remain intact while the users of the old website can still find the content they are looking for.
How Redirect Chains are Created?
Redirect chains and loops are created when the website owner is not careful while implementing 301 or 302 redirects. Two common reasons for how redirect chains are created include:
Oversight
Sometimes redirects are not noticeable to the human eye, while other times, we tend to overlook them. This means if there’s a redirect in place that you don’t know about and create another one, you’ll end up creating a redirect chain.
However, many times, marketers knowingly create a redirect to an existing redirect without giving a thought to its long-term effects because it saves time and effort, and serves their purpose.
Platform Migrations
After performing website platform migration such as from Magento to WooCommerce, most website owners or developers would forget about the old redirects and implement additional ones. This would create unintentional redirect chains and loops that are hard to notice and find at a later stage.
How Do Redirect Chains Affect SEO?
Before we get to know redirect chains SEO effects, let’s first answer how many redirects in the chain are too many.
Well, for starters, each search engine has its own limitations regarding how many redirects there should be in a chain. Since Google is the most used search engine, it aborts a redirect chain after five hops. Also, John Mueller at Google has recommended less than 5 hops per redirect chain.
This means if your web page has more than five redirects in a chain, Google won’t pursue it further to save its crawling resources.
Thus, you should always make sure that there isn’t a redirect chain at all or it should end within 2-3 hops.
Now to the main point, if the redirects are set up in a way that creates a redirect chain, it can negatively impact your website's SEO. The main issue with redirect chains is that they slow down page load times, which can frustrate users and hurt your website's ranking.
Here’s how redirect chains can impact your SEO:
Slow Page Load Times: Since each redirect in a chain adds an additional HTTP request, it can make pages slow, leading to user frustration. Also, search engines like Google consider page speed as one of the important ranking factors. Thus, sluggish page load times due to redirect chains can greatly impact your website's SEO and ranking.
Lost Link Equity: The primary reason to redirect an outdated page to a new one is to pass on the link equity from the original page. However, with multiple redirects in a chain, each redirect can dilute the link equity, leading to a loss in ranking for the destination page.
Penalty from Search Engines: Redirect chains are a sign of poor website maintenance or search engines may flag it as an attempt to manipulate search ranking. This can lead to a penalty that can negatively affect a website's SEO.
Confuses Search Engines: Redirect chains can confuse search engines and make it difficult for them to crawl and index your website's pages. This can lead Google to not properly index and rank your pages in SERP.
Wastes Crawl Budget: Google crawls only so many pages of a website on any given day based on its crawl budget. Redirect chains can exhaust this budget, wasting the crawl budget by sending crawlers on multiple URLs to access one page. This may not be an issue for smaller sites, but it can definitively affect large sites such as Fashion as Google can’t properly crawl and index them.
How to Find Redirect Chains on Your Website?
To avoid creating a redirect chain, it's important to set up page redirects correctly and avoid creating unnecessary ones. However, redirects created in unavoidable circumstances can easily be located using tools like website crawlers to identify and fix redirect chains on your site.
Here’s how to find redirect chains on your website:
Use Crawling Tools to Check for Redirect Chains
So many paid and free crawling tools are available that allow you to audit your website to detect any technical issues and redirect chains. Here are a few tools to give a try:
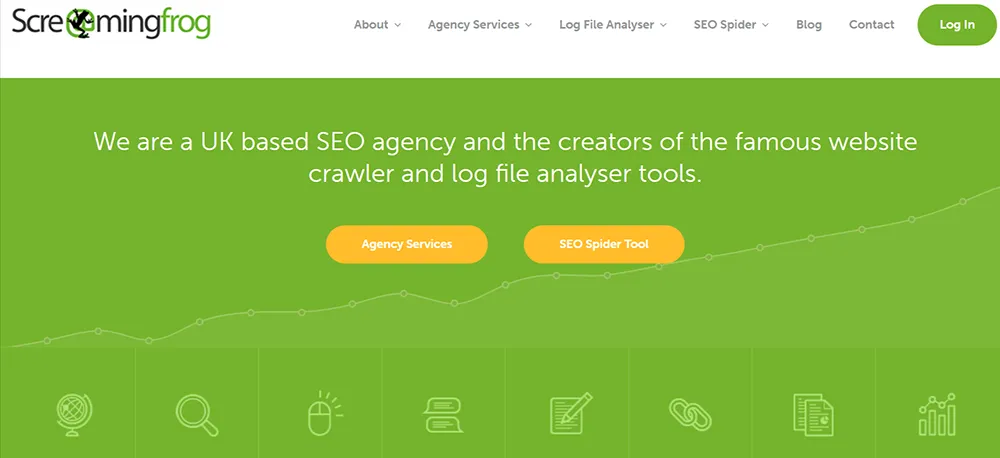
Screaming Frog: The SEO Spider offered by Screaming Frog lets you audit your website to discover bad redirects, broken links, duplicate content, and many other things. The free version of redirect chains Screaming Frog tool allows you to crawl up to 500 URLs and the paid version offers unlimited crawls.
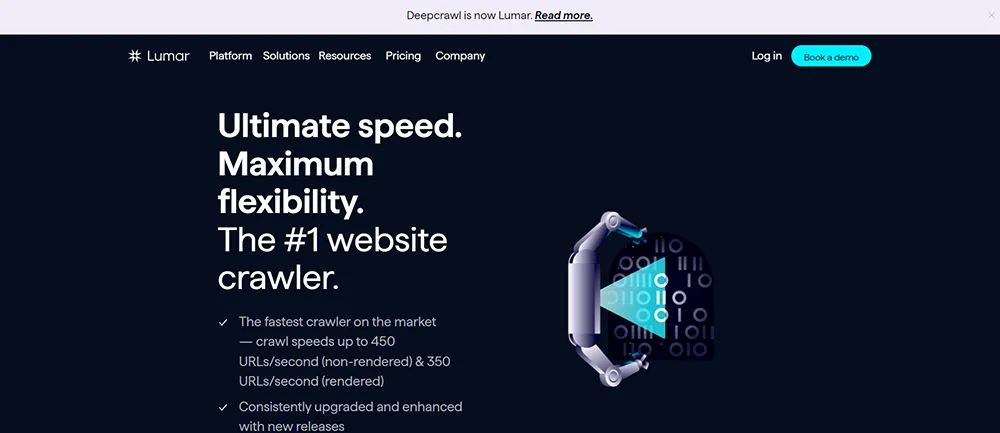
Lumar: Lumar — formerly known as DeepCrawl — offers the fastest website crawler on the internet with speeds up to 450 non-rendered URLs/sec and 350 rendered URLs/sec. The crawler provides all the crawl-related issues with your website including redirect chains.
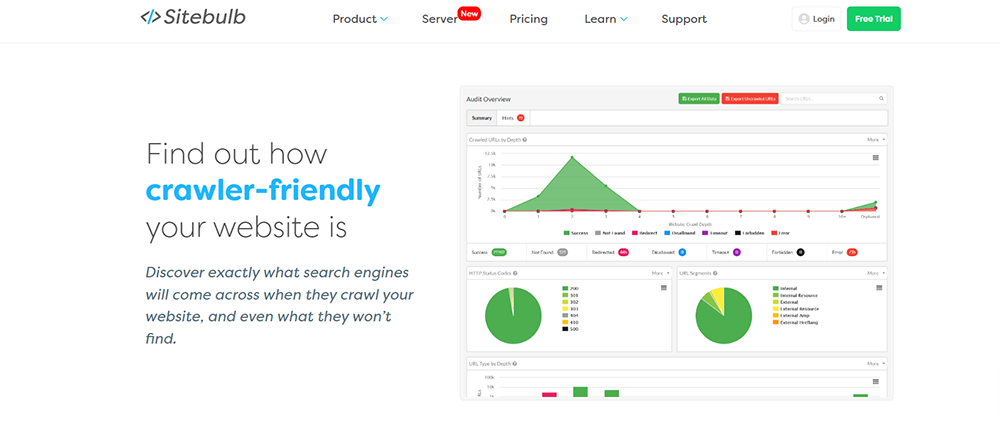
Sitebulb: Sitebulb is another great SEO tool that offers a host of reports including finding issues with redirects and external links. The tool will crawl everything it discovers and help you find problems with your redirects or broken links.
Redirect-checker.org: It’s another simple online redirect checker tool you can use for finding 301 or 302 redirects for specific pages. Just enter the URL of the page and it’ll show the results. However, the only drawback is you can’t check the entire site in one go.
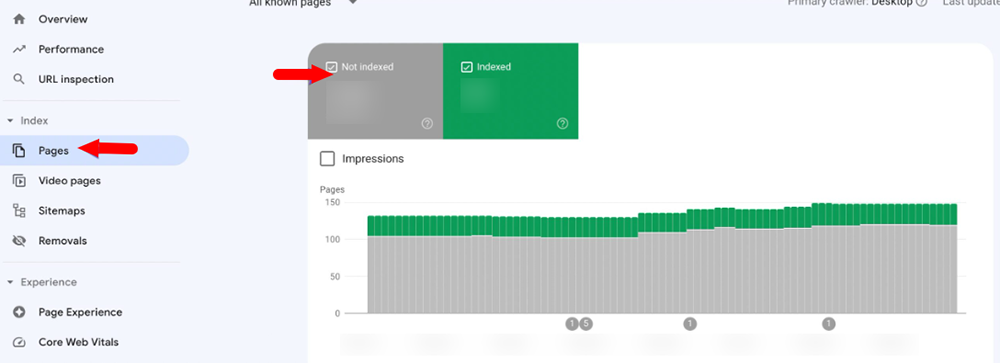
Google Search Console: Another best way to find pages with redirects is to use Google Search Console. Navigate to the Pages section from the left panel and click on the Not Indexed tab at the top. On the next page, you’ll find “Page with Redirect” listed as a reason, which shows you the list of pages with redirects.
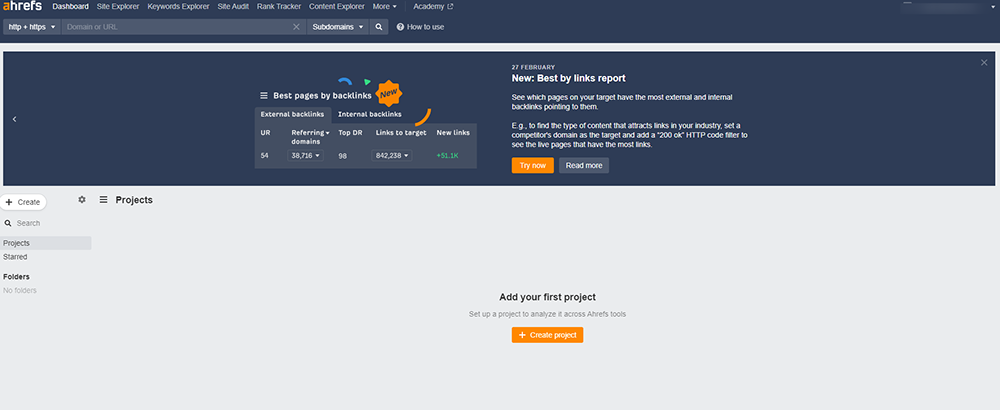
Ahrefs: Using Ahrefs’ Site Audit tool, you can access the Redirect Chain error for your website. To do so, check the Internal Pages report and find the “Redirect Chain” error. Clicking this will reveal all the URLs with a series of redirects and their final destination.
You can choose any website audit tool based on your needs and budget and begin scanning your website for redirect chains. After scanning your site, the tools provide you with a list of URLs that correspond to HTTP status codes such as 301 and 302 that indicate a redirect exists.
Once you get your hands on the redirect chains on your website, it’s time to remove them and free your website from any troubles.
How to Fix Redirect Chains and Loops?
By fixing redirect chains, you can improve page load times, preserve link equity, and recover from search engine penalties which ultimately leads to better SEO. Fixing bad redirect chains starts with identifying ones, which we’ve covered extensively in the previous section.
Now that you have a list of redirect chains, removing them is simple as you only need to cut down the middle redirects and change the first URL’s redirect link to the final URL.
For example, if a redirect chain involves Page1>Page2>Page3, then redirect Page1 to Page3 by eliminating the redirect to Page2.
However, in doing so you may risk losing backlinks associated with Page2, so consider leaving Page2>Page3 redirect intact. If Page2 is only to act as a bridge between Page1 and Page3, consider removing the redirect entirely.
Remember that every redirect you create is going to cost some link equity, thus, be mindful when creating redirects and redirect chains. However, you can prevent redirect chains from building up by frequently checking your site using the tools mentioned above.
Break Free of Redirect Chains
As explained above, redirect chains can have a negative effect on your website’s SEO and cause user frustration. They can slow down the page load time, create confusion for search engines, and take away link equity.
However, you can avoid these issues by setting up correct redirects, avoiding unnecessary ones, and regularly check redirect chains. Doing so helps you improve the user experience and may not hurt your website SEO, leading to better results in Google SERP.
Remember that good website maintenance and SEO practices require constant attention and effort. That’s where SEO agencies like Supple come in to help you lead a healthier and well-structured website.
Contact us to consult with our SEO professionals for all your redirect and other technical SEO issues and get immediate remedies to run a better and well-optimised site.
DIGITAL MARKETING FOR ALL OF AUSTRALIA
- SEO AgencyMelbourne
- SEO AgencySydney
- SEO AgencyBrisbane
- SEO AgencyAdelaide
- SEO AgencyPerth
- SEO AgencyCanberra
- SEO AgencyHobart
- SEO AgencyDarwin
- SEO AgencyGold Coast
- We work with all businesses across Australia