JavaScript SEO: 6 Experts Share Best Practices and Tips to Stay Ahead in The Game
Getting your website crawled, indexed and ranked on the SERPs is easier said than done.
Right from the crawling part of the process, you have a lot of considerations and optimisations that you will need to pay heed to. All this becomes slightly more complicated when you have a website that relies heavily on JavaScript.
After all, we have all been warned about the ill fate faced by many JavaScript-based websites on Google SERPs. But before you call an SEO agency to your aid, this scenario has been evolving for quite some time. With Google introducing its own JavaScript framework – Angular, and issuing guidelines that JS-based websites can use to rank well, we know that Google is warming up to JavaScript.
But there is no doubt that you will need a strong SEO strategy — a JavaScript SEO strategy to navigate this process. So, let’s first establish what this strategy means and entails.
What is JavaScript SEO?
Let’s start with defining what JavaScript SEO is.
JavaScript SEO will usually be categorised as a part of your technical SEO efforts. It aims to make websites that are heavy on JavaScript easy to crawl and index. Ultimately, it exists to serve the same goal as any other SEO activity or task — making your website (JavaScript-heavy) rank higher on the SERPs.
At this point, you may wonder what all the fuss is about — is JavaScript good for your SEO strategy or not?
Well, JavaScript SEO definitely has a bit of a learning curve making it slightly more complex than regular SEO. But get it right, and you have nothing to worry about. Just remember that JavaScript is a lot heavier than HTML and CSS, and if you use it extensively, you may very well be trading your performance for functionality.
So, does your JavaScript affect SEO or SERP performance? What is this bittersweet relationship between JavaScript and search engines?
Stay with us as we will be uncovering answers to these questions and more in this JavaScript SEO guide with the help of experts in the upcoming sections.
Understanding Google and JavaScript
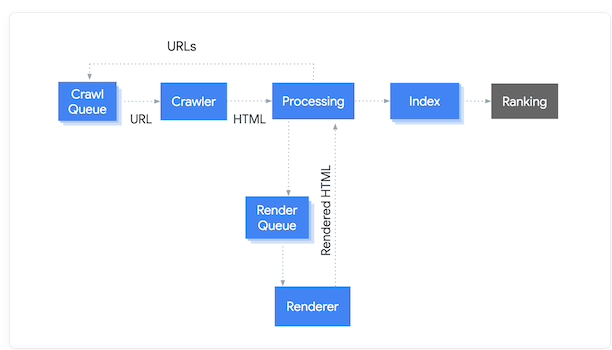
To understand the mechanics between Google and JavaScript, you will first need to know how Google crawls, indexes and ranks websites such as yours. Several processes and sub-processes interweave in the journey, from the discovery of your website to ranking on the SERPs. But here’s a simple illustration of the key processes:
The Crawl Queue contains all the URLs that need to be crawled by Googlebot. The crawler receives URLs from the Crawl Queue, and the indexing needs are assessed. Simultaneously, the need for rendering is assessed based on the website’s reliance on JavaScript.
Every URL that needs to be rendered is added to the render queue, which then prompts the renderer to render the URLs and sends the rendered HTML to index them. While most URLs go from the crawl queue and move on to getting indexed, JavaScript-heavy websites have to go through an additional rendering process.
This makes the whole process of crawling and indexing JavaScript-heavy websites comparatively inefficient and slow compared to others. Now if you have a comprehensive BigCommerce online store, think about the amount of time Google will spend rendering and indexing thousands of pages. To make the whole process more efficient, you will need to keep on optimising your website and check whether its reliance on JavaScript is slowing it down.
You can use tools such as Google Search Console, Mobile Friendly Test and Rich Results Tester to check whether your website is optimised and can be crawled and indexed effectively.
You don’t have to worry about using JavaScript on your website anymore. You are only likely to miss out on opportunities if you use JavaScript on your website in a way that requires users to interact with it.
For example, a button that requires users to click for the content to be rendered. This is not a great practice because Googlebot does not interact with any elements on your website while crawling it.
It is also important to understand DOM (Dynamic Object Model) when we talk about JavaScript in the context of SEO. DOM acts as a layer between the page code and what is displayed on the screen. Basically, what you see when you use “Inspect Element” on your website is DOM. It is a major factor when it comes to updating the content of the website after it has been rendered on the screen.
The impact of JavaScript on DOM is what makes it so vital to be used in dynamic and advanced websites today.
JavaScript SEO: Best Practices and Tips
We will now talk about some of the best practices and tips that you can use to stay at the top of your SEO game, even with a JavaScript-heavy website.
#1 Add Links and Images as per Predefined Standards
Google discovers all the webpages and understands your website architecture with the help of links. It is important to consider that all the navigational and contextual elements on a website are contained within links that you integrate into your website.
A potential SEO issue can be created when links are internal or if JavaScript creates links to a URL when users click on it. This is because Google will be unable to discover such links. The only solution to this issue is to have descriptive anchor texts to your links and add href attributes. Avoid using <div> or <span> tags for important web pages as they are not crawled.

“Content creators can still encounter some issues when it comes to links and facets. If those are present in the sites you manage, you definitely need to check if all of your content is being presented to search engines in the way you want it to.”
If Google is not able to crawl your JavaScript links, you will be missing out on a crucial amount of link juice. Hence, it is highly recommended that you keep links as static HTML elements to make them easily discoverable.

“Well, by my opinion prepare content, images and links crawlable just with HTML which should be rendered on server.”
Along with these considerations for links, it is also highly suggested that you lazy-load your images. This will help your JS-dependent web pages to load quickly even if just with the core content and then the images can follow.
#2 Utilise Server-Side Rendering
We have already talked enough about rendering for you to know that it takes up a lot of time and resources. There are two types of rendering that you should consider before we go further and discuss them in the context of JavaScript SEO.
- Server-Side Rendering: Also known as SSR, server-side rendering is the ability of an application to render HTML files on a server into a fully rendered page ready to be displayed on your browser.
- Client-Side Rendering: Also known as CSR, client-side rendering is a new type of rendering which is the ability of an application to render information using JavaScript with the help of a browser.
Now that you have an understanding of these two methods, you can guess the impact they have on the indexing and ranking of your website. We have already discussed the existing bottlenecks in the process of crawling, indexing and ranking a JavaScript-heavy website.

“If something breaks in the JavaScript or if the scripts take too long to execute, then Google wouldn't be able to see the content produced by that JavaScript. That's fine if the content is secondary, like for additional features on the page. If that JavaScript failure causes core content on the website to not load, then Google will see empty pages. Websites with these kinds of issues end up with lots of pages not indexed and a loss of traffic.”
However, when you use server-side rendering, all your content will be displayed with HTML markup. So, Googlebot will not have to return to index the JavaScript-based content on your website, thus easing your JavaScript SEO strategy.

“I'd always suggest using server-side rendering for any important content. If you have to use client-side rendering (not preferred), make sure you aren't blocking access to JS files for bots. Don't block "necessary" JS files that is. Stuff like marketing and analytics tracking isn't necessary.”
#3 Optimise Website for Speed and Performance
As you begin to work on improving your website performance, you will hear a lot about optimisation and the various things that you can do. But make no mistake — improving your website speed and performance will be at the top of that list and for good reason.
The speed at which the pages on your website load can make all the difference between a customer engaging with your content, and abandoning it. No wonder, page speed is one of the most important signals pinpointing the kind of experience your website is delivering. Plus, you need to take into account the implications of a slow-loading website on its crawlability and rendering.

About this, Matthew Edgar further says, “One of the primary reasons Google is not able to successfully load and execute JavaScript files is that the files take too long to load and execute. As you think about website speed, it's very important to make sure that critical JavaScript functions--the functions loading essential parts of the page that Google needs to see--load quickly.”
You can take multiple steps to solve this issue. You can firstly minimise the usage of JavaScript on your website. You can also defer any non-critical usage of JS till the main elements on your DOM are completely loaded. Additionally, you can also consider serving it in smaller payloads to avoid putting too much load on your website.
To ensure that your website loads and functions quickly, use website speed tools to measure and analyse its performance.
#4 Test Your Website Regularly Using Tools
One of the best parts about implementing Javascript SEO in this day and age is the possibility of using the myriad tools out there. Testing your website periodically is not optional if it relies too much on JavaScript.
In fact, it is highly recommended that you use tools such as Ahrefs or SEMrush when you are trying to gauge the impact of JavaScript on your website's SEO performance.

When asked about the top JavaScript SEO tools that he relies on, Peter Rota, Senior Technical SEO Manager at HUB International, quips, "I'm currently using a mix of the web developer chrome extension and Inspect URL in Search Console. If you don't have access to search console, you can either use the rich results test or a mobile-friendly tool."
On your journey to optimise and debug your JavaScript SEO efforts, you will also use several rendering tools such as Puppeteer and Prerender. What’s more, apart from these rendering and Google tools that we have discussed so far, you will also likely use tools such as URL Inspection Tool or WWJD (What Would JavaScript Do) in the process.
There are tools that you can also use when you are conducting technical SEO audits or JavaScript SEO audits, in order to ensure that your JS-dependent website is optimised.

Peter Rota further suggests, “Currently, I use screamingfrog when I'm doing my tech SEO audits. Then I will just have it render javascript via Google's smartphone bot. But, you should be fine as long as the crawler or tool you use executes javascript.”
Apart from these tools, we also recommend using Screaming Frog SEO Spider to monitor the crawling, indexing and rendering of your JavaScript-heavy web pages.

“I crawl the site using HTML in Screaming Frog, and then switch to JavaScript crawl and see if there's any differences. I have a plugin called "Chrome Dev Tools" that I use to toggle stuff like JS and CSS on and off to see how the site responds. You can find a lot of stuff that is potentially an issue by poking around the site and there's still nothing I've found that can beat sampling pages in developer tools after you do your crawls. If I have Search console access I'll also fetch and render a few pages (and view their cache) in Google to see how they're seeing the site.”
#5 Leverage rel=canonical
Canonical tags and URLs help search engines find the main page within a group of duplicate pages. They also prevent the crawling of duplicate pages on your website and consolidate the link juice from multiple URLs.
When you inject canonical links through JavaScript, it can cause quite a storm in your website, considering Google will discover these pages only after they are indexed and rendered. So you could really lose out on the crawl budget and resources if you do not include the canonical URL in the initial HTML response.
To prevent this, you should consider using important directives in the initial HTML response such as the following:
- link rel="prev"/"next" attribute
- link rel="alternate" hreflang attribute
- link rel="alternate" mobile attribute
Google also recommends that you do not use JavaScript to inject rel=canonical tags in your URLs. However, there is a way to ensure that Google will pick up the injected canonical URL when rendering the page with JavaScript.
It helps to understand the process deployed by Google in detail to deal with canonicalisation so that you can leverage it to empower your JavaScript SEO strategy and not the other way around.
#6 Use Pagination
At this point, we need to emphasise the importance that pagination holds, especially in the context of JavaScript eCommerce websites. Right from eCommerce content optimisation to adding advanced intuitive features, online stores put in a lot of effort to level up their user experience. Now, infinite scrolling might seem like a good idea when you are making UX a priority, however, it can be easily detrimental to the website’s SEO performance.
Since Googlebot will be unable to trigger events to load more content on such pages, it will eventually stop scrolling and leave your page — meaning some of your crucial content might get ignored.
The simple solution to this challenge is using href attribute to help Google discover and see the second page of your pagination.
#7 Allow Googlebot to Crawl Your JavaScript
Unfortunately, there have been several instances wherein eCommerce websites have accidentally or otherwise blocked JavaScript files from crawling.
If you end up doing this for your website, you would be actively preventing Googlebot from indexing and rendering that piece of code. To avoid this situation, it is highly recommended that you regularly check your robots.txt file to ensure that all the JS files are open and available to Googlebot for crawling.
#8 Ensure Rendered HTML Includes Necessary Information
While we have previously highlighted the need to include vital information in the initial HTML response when your website relies heavily on JavaScript. The reason is simple — if you absolutely have to have search engines render your web pages, the least you can do is have the necessary information easily accessible in the initial HTML response.
This necessary information includes meta tags, such as titles and meta descriptions, which should be integrated into the <head> section of your HTML code. The other important body content can then be introduced using JavaScript.
Say, you have a website for your plumbing business in Adelaide, where you post blogs and content regularly. Even if you get creative with the kind of graphics and elements you add to your website, you want to have all the meta tags established in the initial HTML response to help search engines index these pages.
This will ensure that Googlebot has all the crucial information necessary to crawl and index your webpage right off the bat, making a first good impression.
#9 Utilise Code Splitting and Lazy Loading
Code splitting and lazy loading can be your best friends if you are trying to ensure that your website quickly loads and your user experience is not compromised. We talked about lazy loading briefly when we discussed page speed and performance. However, you will need to know how to leverage it right, if you want to level up your JavaScript SEO strategy.
Deferring loading of non-critical components of your website till the most core content is rendered and loaded is considered to be a common UX practice. This practice is also highly recommended to ensure your JS code does not slow down your website performance or derail it in any way.
Code splitting is a process that will help you break your code down into pieces that can be loaded on demand. As applications grow in size, so do their JavaScript bundles and code splitting ensures that you do not end up compromising your website performance and speed because of such elements.

“We have found code splitting to be quite useful for websites that have multiple JS-based elements. It helps you distinguish the core content that needs to be rendered immediately when the URL clicked by the user is loaded. It is also one of the easier wins in your JavaScript SEO strategy.”
You can leverage code-splitting to ensure that the core content loads without any kind of delay. Meanwhile, lazy loading will ensure that all the JS elements are loaded onto the page only after these crucial elements or content blocks are fully loaded.
#10 Use the History API instead of URL Fragments (#)
Google can only crawl links that are provided in the form of the href attribute in the HTML element. URL fragments, also known as hash URLs, are completely valid, however, do not always work as intended with the Googlebot.
When URL fragments are used to redirect the user’s attention to a specific part of the content on the same page, you are using them right. At the same time, if you are using them with JavaScript to load content on other pages, such a technique might not necessarily work with Googlebot — this is not the right way to use URL fragments.
Google recommends using History API instead of URL fragments to migrate web apps to URLs. History API allows users to manipulate the browser session history or the pages that were explored in the current frame or tab in your browser.
When you want to implement routing between different views of your application, you should utilise History API. Fragmented URLs may not be a great idea in this case, because it will lead Googlebot to parse and extract URLs. Using History API ensures that Google can easily access your URLs.
Empower Your JavaScript SEO Strategy
With that we have come to the very end of our JavaScript SEO guide. We are sure that you will find several of our prescribed best practices useful and applicable to your website. Making your JavaScript-dependent website rank is not easy, but it is definitely possible if you get your JavaScript SEO strategy right from the get-go.
But if you find yourself running into issues or confused about your approach towards strengthening your JavaScript SEO, get in touch with us. We will get in touch and help you get your JavaScript SEO aligned with your other marketing efforts.
DIGITAL MARKETING FOR ALL OF AUSTRALIA
- SEO AgencyMelbourne
- SEO AgencySydney
- SEO AgencyBrisbane
- SEO AgencyAdelaide
- SEO AgencyPerth
- SEO AgencyCanberra
- SEO AgencyHobart
- SEO AgencyDarwin
- SEO AgencyGold Coast
- We work with all businesses across Australia