12 SEO Tips for Web Developers
As a web developer, you’re obviously more focused on getting your site to function properly than worrying about how to get traffic to it.
However, from a business perspective, even a perfectly-functioning website is a redundant resource if there’s no traffic since you can’t drive revenue from there.
So, no matter how well-designed your site is, it needs to appear in search results for your audience’s queries.
At the same time, a well-optimised and ranking website with a poor design & UX would eventually lose its ranking and traffic as search engines like Google prioritise users over anything else.
Thus, web development and SEO have become more integrated today than ever before. And they both must come together to create a successful website.
In this article, we’ve shared the 12 important SEO tips for web developers. Whether you’re a solopreneur developing your own website, an in-house web developer or a freelancer, keep these SEO tips in mind while creating a website.
Why Does SEO Matter for Web Developers?
Web developers need to understand SEO thoroughly because SEO is not only about content creation and on-page optimisation. Other factors like user experience (UX), code development, licences & approvals, etc. also influence SEO.
Simply put, how you design and develop your site also affects its performance in search results.
Thus, SEO is not just the responsibility of your SEO team. It also requires involvement from non-SEO teams like web design & development, product, and content.
Besides, if you optimise your website right from the development stage, it increases the chances of better performance in SERPs.
SEO Tips for Web Developers
Whether you’ve built a website on no-code, drag & drop website builder or coded your way through it, follow these SEO tips to improve your site’s performance on search engines.
1. Understand How Search Engines Work
To create an SEO-friendly website, you must first understand how search engines work.
Let’s take Google for instance.
Here are the three key stages of how Google Search functions:
- Crawling: A team of bots (also known as crawlers or spiders) scour the internet to find new and updated content—webpages, images, videos, PDFs, etc. This process is called Crawling.
- Indexing: Then, Google stores and organises the content found during the crawling process into their Search Index—a digital library of webpages.
- Ranking: When a user types a search query on Google, it returns the results that best answer the searcher’s query. The most relevant page is ranked at the top and so on.
The main factors that Google considers when ranking the search results is the meaning, relevance, quality, usability, and context of the webpages that answer the user’s search query.
So if you analyse and understand how search engines work, you can create a site that meets the search engines’ basic requirements.
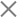
2. Create User and SEO-friendly Site Structure
Use a simple, flat site architecture while building your website. A flat site structure means users can reach any page on your site in three to four clicks maximum.
Here’s an example:
A simple and flat architecture helps users navigate through your website easily. Besides, it also makes it easy for Googlebot to crawl your site. Consequently, it optimises your crawl budget—Googlebot can crawl more pages from your site in a single crawl session.
If you don’t have an in-house SEO team, you can hire external SEO services to help your web developers create an SEO-friendly website.
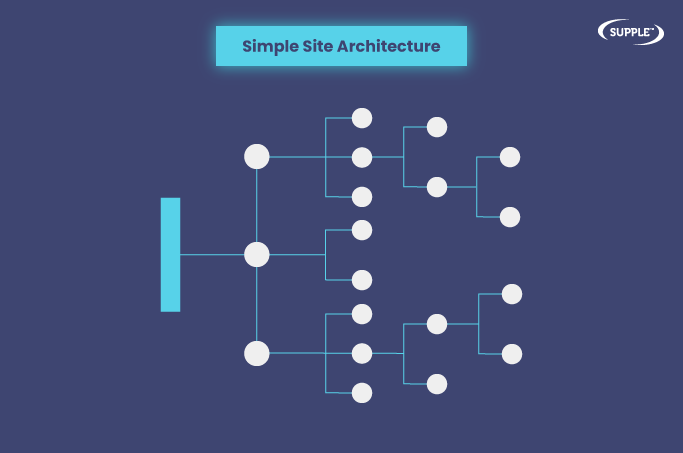
3. Submit Sitemaps
Sitemaps as the name suggests, act as a roadmap for your website. An XML sitemap helps search engine crawlers and an HTML sitemap helps users navigate through your site.
Googlebot can read an XML sitemap and easily access the URLs included in it. So you must include all the important webpages in your XML sitemap and submit it to Google using the Search Console.
This is what an XML sitemap file looks like:
Ideally, you should only include the URLs of the pages that you want Google to crawl and index.
Similarly, create an HTML sitemap on your website for your users. Typically, HTML sitemaps are added to the footer section of a site.
4. Optimise Website Speed
A slow-loading website harms your SEO and conversion rates.
Take a look at the below statistics on site load times and its effect:
- 25% (1 out of 4) visitors abandon a website if it takes more than 4 seconds to load. This would increase your bounce rate and hurt your SEO.
- 46% of visitors wouldn’t revisit a poorly performing site. Thus, it negatively impacts future business opportunities too.
- Conversion rates drop by 4.42% with every one-second delay in page loading time.
So test your page performance with tools like PageSpeed Insights or WebPageTest and optimise your site speed if needed.
Here are some quick tips for site speed optimisation:
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Write a mobile-first code for your site
- Select a reliable hosting service
- Optimise images
- Minify and Combine CSS, JavaScript, and HTML Files
5. Install SSL Certificate
An SSL certificate can help you move your website URLs from HTTP to HTTPS protocol. HTTPS protocol lets you keep your users' data secure with encryption and verify your server identity.
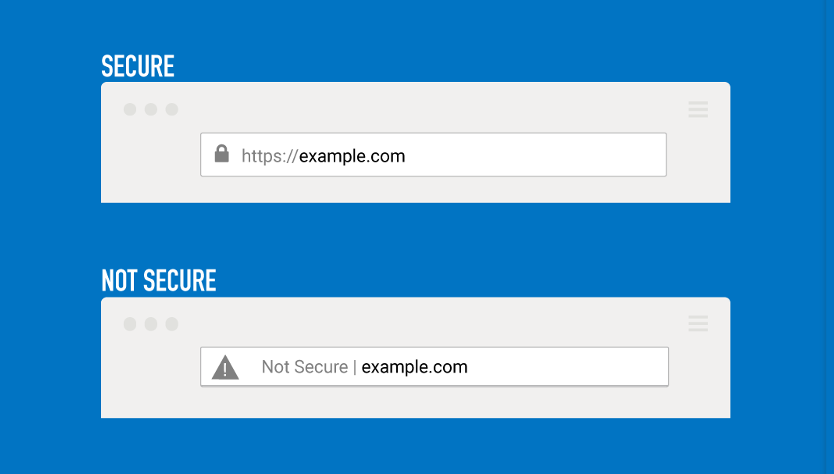
Here’s what the URLs with and without SSL certificates look like:
As you can see in the image, browsers also show a warning “Not Secure” in the address bar. Some browsers also show this warning as a pop-up before loading the page and ask users if they still want to visit the page.
And most visitors would leave such sites due to security concerns. Hence, you must get an SSL certificate for your site and generate trust signals to users and search engines.
6. Create Reader-friendly URLs
You can make your URLs effective by writing them in a descriptive yet concise manner.
The basic idea is: The URL should indicate (succinctly) what the page is about as it helps your users and search engines understand your page.
Here are some tips to help you create reader and search-friendly URLs:
- Add the primary keyword in the URL slug
- Write URLs in lowercase
- Write a concise URL slug (three to four words)
- Avoid using space or special characters
- Separate the words in the slug using hyphens
7. Get a Grip on Redirects
Whether you’re a freelance web developer, a website development agency, or an in-house developer, it’s important for you to have a thorough understanding of redirects.
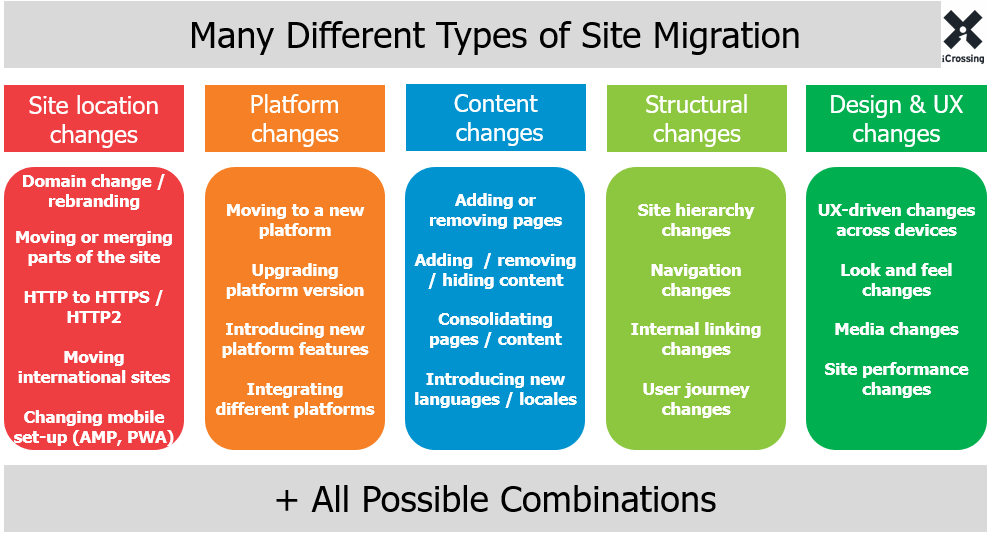
Sometimes you may need to perform site migration while changing CMS platforms or making design & UX changes. So during the migration process, you may need to redirect your pages temporarily or permanently.
There are many types of site migrations as you can see in the below image.
Apart from site migration, you may also need to redirect your pages for other reasons like content consolidation, deleting pages with duplicate content, moving URLs, etc.
The two most commonly used types of redirects are:
- 301 redirect: It’s a permanent redirect. When you 301 redirect a page, it’s removed from Google Search Index and it shows the new (destination) page in search results. And it also transfers the page authority (PageRank) to the new URL.
- 302 redirect: It’s a temporary redirect. In this case, Search Index retains the old URL and shows the old (source) page in the search results. Once the user clicks that page, they’re redirected to the new URL. Also, the PageRank is retained by the source page.
8. Keep a Check on Server Response Codes
Server response code—also known as HTTP status code—is the server’s response to the request from the browser.
Here are some of the essential server response codes you should know as a web developer:
- HTTP 200 OK: It means that the browser request was successful.
- HTTP 301 Moved Permanently: The URL is permanently redirected to a new page.
- HTTP 302 Moved Temporarily:The URL is temporarily redirected to a new page.
- HTTP 404 Not Found: The requested page couldn’t be retrieved. This could be temporary or permanent.
- HTTP 410 Gone: The requested resource can’t be found and won’t be available permanently.
- HTTP 500 Internal Server Error: It indicates that there’s an issue with your server.
- HTTP 503 Service Unavailable: It means the server might be overloaded or under maintenance and it’ll be back soon.
Ideally, you want an HTTP 200 OK response for all the pages (especially important pages) on your site unless you’ve removed or redirected them.
So conduct an SEO audit of your website periodically to ensure that pages are loading correctly.
9. Use Robot.txt Files
When you want to lock away some pages from being crawled and indexed, you can inform search engines about them by using a robot.txt file.
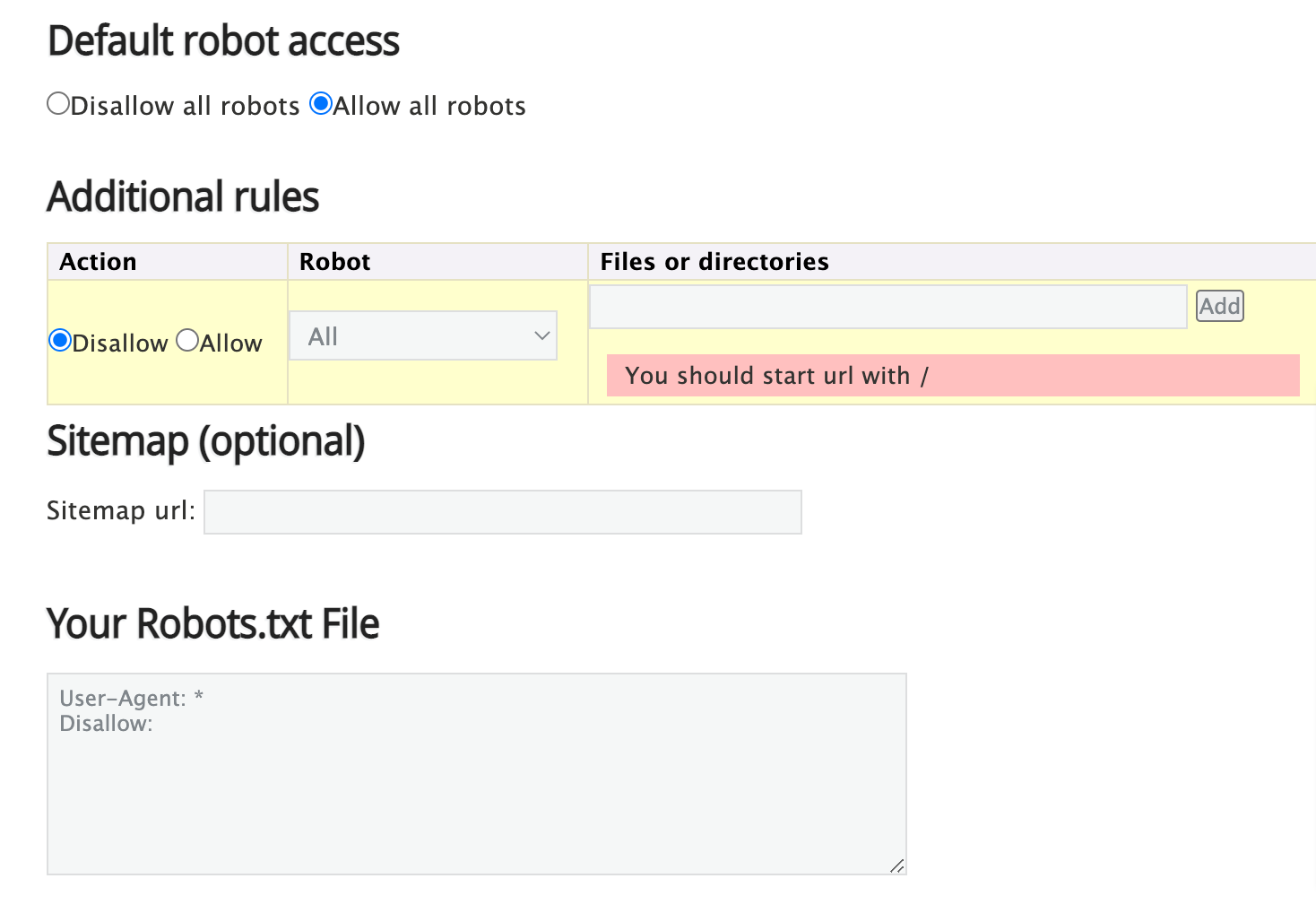
For example, you may want to prevent the crawling of duplicate pages, thank you pages, internal search pages, etc. Now, you need to create and submit a robot.txt file to disallow Googlebot from crawling these pages. Refer to this robot.txt guide from Google to understand the entire process.
You can create a robot.txt file in a blank .txt document and specify the crawling rules as mentioned in the above guide. Or you can simply use a robot.txt generator tool and add rules in the relevant sections as shown in the image.
If you’re new to robot.txt files, it’s better you let your technical SEO handle this task because even a small error here can cause big damage to your SEO efforts.
And if you don’t have in-house technical SEO expertise, work with an experienced SEO agency to help you with robot.txt files.
10. Optimise for Mobile Devices
As per the statistics, nearly 59% of web traffic globally comes from mobile devices. Hence, when you develop a website, make sure that it works well on desktop and mobile devices alike.
You can use Google’s Mobile-friendly Test Tool to check how your website works on mobile devices.
Besides, here’s how you can optimise your site for mobile users:
- Use a custom CSS for better responsiveness
- Check if your themes and plugins are working properly on mobile devices
- Create custom pop-ups for mobile site
- Test your website’s Core Web Vitals, check the diagnosis report, and take necessary action (if required)
- Optimise your website loading time
11. Design a Custom 404 Page
We all encounter broken or 404 error pages at some point. Just like you expect the right page when you click a link, your users also do.
However, it’s not always in your control that users land on the right page on your site—especially when they’re coming to you from a link on an external site.
If there’s a minor error in entering the URL while linking, the intended page won’t load and show an error message.
At times, you may have taken off the page and forgotten to redirect that URL to some other relevant page.
Whatever the case, the 404 error page doesn’t necessarily have to be boring like this:
Let’s admit it! It’s a negative user experience irrespective of the cause of the error.
With a little effort in customising this error page, you can neutralise the negative impact. Here, you can at least place a copy that either helps (by including links to the homepage, products/services, blog, etc.) or entertains (with a funny message) users.
Some websites even convert such instances into an opportunity by offering some additional value.
For example, see how Ahrefs leveraged their 404 page to explain “broken link” and converted it into a free product-trial offer.
Similarly, think about what you’d like your users to see when they land on your 404 page and design it accordingly.
12. Externalise JavaScript and CSS
While crawling a site, crawlers prefer to access the content as soon as possible.
However, if you’ve placed your JavaScript and CSS inside the HTML document, it adds additional lines of code in HTML. Most likely, these codes will be placed ahead of the main content and may slow down the crawling process.
Hence, externalise the JavaScript and CSS while you’re coding your site.
Wrapping Up
The whole idea behind investing in a business website is to establish your brand’s digital presence, attract visitors and convert them into customers. And all these depend heavily on how your site performs on organic search.
Hence, SEO is going to be an ongoing process for your website to perform well on search engines. But if you set the foundation right while creating a website, it aids your SEO performance.
So if your web developers are familiar with SEO basics, there’ll be fewer SEO-specific rework requests. Also, it’ll make the overall development process more efficient.
That said, if you need expert SEO consultation for developing or migrating your business website, do reach out to us. We’re here to help.
DIGITAL MARKETING FOR ALL OF AUSTRALIA
- SEO AgencyMelbourne
- SEO AgencySydney
- SEO AgencyBrisbane
- SEO AgencyAdelaide
- SEO AgencyPerth
- SEO AgencyCanberra
- SEO AgencyHobart
- SEO AgencyDarwin
- SEO AgencyGold Coast
- We work with all businesses across Australia