A Brief Introduction to Entity-based SEO and its Importance
Google has long moved from providing keyword-based results to personalised search results through its Knowledge Graph update. Google has been working on it since 2012 to provide an intelligent model that understands real-world entities and their relationship with one another.
This knowledge graph helps searchers find things, people, or places that Google has knowledge about. For instance, locations, landmarks, cities, humans, objects, celebrities, sports teams, buildings, movies, celestial objects, and others.
Knowledge Graph is a massive database built with the help of authoritative sources like Wikipedia, and others. Thanks to that, this decade-old Google algorithm update gave birth to entity-based SEO.
Entity SEO has demonstrated websites moving beyond just the standard search box and thinking outside the box. They emphasise more on the context, user intent, and relationship between words that make up entity search SEO.
But what does it mean and why it matters? If it’s bugging you, let’s dive deep into it to help you make sense of what it is.
What is Entity-Based SEO?
Entity SEO goes beyond just keywords to use the intent and context to deliver personalised search results and help users find the information they seek. Search engines like Google are getting smarter the day by day to generate the most accurate results.
It is a fact that machines can’t understand certain nuances and languages that humans can easily comprehend. Search bots often process the phrases but entity SEO helps connect entities by developing a knowledge graph from various authoritative sources.
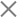
For instance, when you Google search for “Best Batman Movie Actor”, it’ll present you with a list of all the actors that have played the role of Batman in different movies.
Keywords are still essential for SEO but they don’t completely reflect human emotions. From the above example, we can see that the user wants to know the best Batman movie actor, and Google presented a list of several actors who played the role.
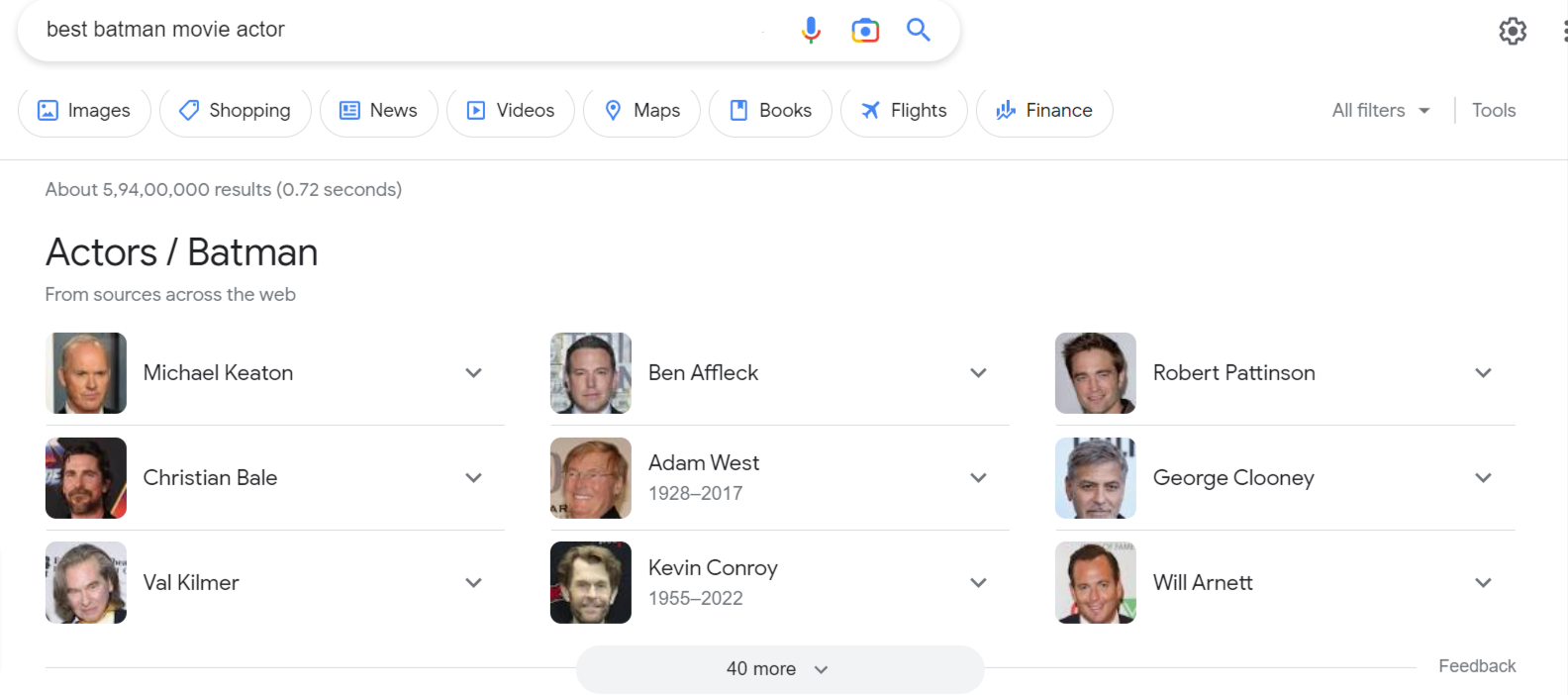
But when you enter the query “who played shiny vampire in Twilight”, it’ll return the knowledge graph on the actor Robert Pattinson (who also has donned the role of Batman).
Thus, Google will present the best possible results for searchers on its knowledge graph and will also offer additional context to serve multiple purposes. Doing so speeds up the process and lets the users move on to the next searches they want to make.
Google describes an entity as a single, well-defined, and unique thing or topic, — helpful to know the content perspective. You can think of entities as topics that are well-defined by other referencing sources and related things.
However, there are still plenty of other interpretations of an entity and it doesn’t need to be a physical object or a word. Entities stand on their own and can be located using different terms. Some examples of entities include:
- People
- Brands
- Books
- Companies
- Domains
- Colour
- Currencies
- Animals
- Media
- Shows/Movies
- And others
To put it simply, Google now uses entities that can be found in different ways on the internet, rather than asking specific questions. Entities are uniquely defined with broader clues rather than narrow terms to provide the information the search query intends to find.
Why do Entities Matter for SEO?
There are a few reasons why entity-based SEO has become a prime focus for Google search optimisation. Due to the rise of voice and mobile searches, Google had to modify and tailor its algorithm to find accurate results.
Also, relying solely on keywords is not a viable option as entities heavily rely on machine learning to interpret the concepts from the search level. Ironically, thanks to machine learning, Google understands pages and their relationships with entities.
Google entities are better equipped to calculate the probability of meeting search intent with higher accuracy. Additionally, it reduces the reliance of Google on links as a ranking factor and becomes a mechanism to establish entity value.
Thus, you need to consider what level of entity optimisation your site needs to maximise the probability of meeting a variety of search intents to beat your competition in Google SERP.
Keywords vs Entities: Differences
Entities differ from keywords in many ways as keywords are just phrases and entities are unique and distinguishable things or concepts. Keywords are often the focal point of the user search and can vary from a single word to a sentence, or a question.
Entities aren’t physical objects and can include colours, dates, ideas, people, movies, and others. They are distinct from each other and are independent entities or terms.
Keywords still matter because they connect queries to content and boost organic traffic to your site. They have long been the backbone of SEO thanks to their clear and concise nature to populate the search result pages.
But since search engine algorithms have evolved significantly over the years, old SEO tactics are now frowned upon. Google now emphasises entities more than keywords to provide more precise information on its SERP.
However, it hasn’t reached the level of psychic because search engines still need more information to know what entity you are searching for. For instance, Google needs more context when someone searches for “apple.”
If a person wants to know about Apple fruit, getting information about the Apple company would be irrelevant. Similarly, getting information on apple fruit won’t be helpful to the person who wants to buy Apple products.
Thus, entities can be defined as large topics, within which keywords live and provide context to help define entities. So, brands taking an entity-based SEO approach need to know what their entity is all about before creating keyword- and entity-optimised content.
How Do Entities Work in SEO?
According to the “Ranking search results based on entity metrics” patent by Google, it considers four factors for entity search SEO ranking. These include:
-
Relatedness: It helps in determining the relationship between two entities often referenced frequently on the web. Since they are frequently used together and have authoritative properties, Google can present one and the same result for both queries. For instance, courts and lawyers are frequently used together.
-
Notability: Google has provided a simple formula for determining the notability of an entity in the patent. It compares the value of the entity with the higher and the lower in the category using links, mentions, relevancy, and reviews. For instance, a big fish in a small pond will have higher authority than in the ocean.
-
Contribution: It’s a measure of the contribution made by the entity to a topic and determined by external factors such as reviews and links. For instance, a reputed chef’s critical review would have a higher contribution than a normal person’s rant on Yelp.
-
Prizes: This metric is a measure of the prizes such as the Nobel Prize, Oscar, Grammy, or others that entities have received. It helps determine the weight of an entity — the higher the prize, the higher the value is attached to the entity.
How Google Makes Use of Entities?
As explained in the previous section, Google uses a knowledge graph to make connections among different entities. Whenever someone makes a search, Google will run a process to determine the relatedness, notability, contribution, and prize values for an entity and produce a SERP.
This entity optimisation algorithm of Google will examine these four values to create a web connection and make search more efficient for users. Google assigns a unique ID to each entity and turns it into the code to help map the knowledge graph.
The algorithm may not be flawless but is still the most advanced out there to help build context behind entity searches.
Entity-Based Search in Advanced SEO
Now that we know what Google entities are and how they help present precise results to searchers, let’s get to know how it helps in advanced SEO searches.
Since Google establishes strong connections between things to make it explicit which entities searchers have mentioned, it requires a bit of technical help. From a technical SEO perspective, schema markups would help establish strong connections effectively.
Using schemas does not necessarily create entities, but you can use specific identifiers to define distinct entities and their relationships with other entities.
When defined with ID, Google can easily link it to the knowledge graph through the schema markup. In addition to the information found across the web, the knowledge graph provides context when crawling websites.
According to Google, Knowledge Graphs have nodes and edges, where the node represents an entity while the edge represents the connection between entities.
For instance, Robert Pattinson from the above example is the central entity and his relationship with other entities such as Twilight or Batman makes him unique in the world.
By understanding and contextualising the information linked to entities, Google begins to interpret the content and resources across the web.
What Are the Benefits of Entity-Based SEO?
Entity-based SEO dives deep at a granular level to provide refined and relevant results than keyword-based SEO. The approach provides more concrete searchability to marketers and brands to leverage additional keywords that may not have been available earlier.
For instance, users can search for “sports shoes,” “running shoes,” “slip-on shoes,” and others to find their favourite brand of shoes. Here are a few more benefits of entity SEO:
Improved Search Results
The biggest reason for switching from keywords to entities is to provide searchers with precise and relevant search results. Search optimisation is much easier with Google entities for mobile and voice search.
Enhanced Snippets
As seen in the above examples of search queries, Google utilises a knowledge graph to provide rich snippets with entity searches. This allows rich snippets to become more useful to searchers, which further improves their user experience.
Additionally, Google learns from user behaviour to better its search results and refines its algorithm.
Precise Translations
Based on the search settings of users, entity optimisation makes it easier to translate between languages. This helps Google to provide precision translations, synonyms, homonyms, and antonyms of words or queries.
How to Optimise Your Site for Entity SEO?
Now that we have understood the concept of entity-based SEO, let’s dive into how you can entity-optimise your website.
1. Conduct Entity Audit to Fill in Gaps
The first step is to conduct an audit to figure out if your site covers the topics that it should be known for. By performing an entity audit, you take a stock of the entities linked with your brand and compare them with the competitors.
Doing so ensures that you are using entities strongly associated with your brand and finding gaps where you lag behind. Then, you can plan and create such content to fill in those gaps and cover topics your website should discuss.
2. Contextualise Your Content
Entity search SEO is specific and contextual, which helps search engines connect the dots and provide accurate information regardless of the language. One way to contextualise your content is to link information about other relevant entities from knowledge graphs with high E-A-T.
For starters, Wikipedia is the best resource for content contextualisation and is trusted by Google. However, not all entities will be present on Wikipedia and you may have to use other resources such as social media or places where entities are present.
Doing so may not increase your ranking in SERP but would establish your brand as an authority in search. By linking entities, you create the context necessary for search engines to understand your content’s relevance and boost your entity optimisation level.
3. Improve Technical SEO to Gain Visibility
Technical SEO is an important part of SEO besides content for entity-based SEO. It refers to the optimisation of website pages other than the content that helps search engines crawl and index sites effectively.
Think of it as the foundation to rank your website content for entities or the topic it covers. You can improve your technical SEO using,
-
Schema Markup: Structured data such as schema markup standardised the information present on the web page. As mentioned earlier, it does not create entities but defines objects with distinct IDs to establish relationships with other entities.
-
Semantic HTML: It adds meaning to your code and helps machines recognise navigation blocks, footers, headings, videos, tables, etc.
-
Sitemaps: Sitemaps provide the list of URLs on your website, which helps search engine bots crawl your website faster. Apart from URLs, it also has details such as importance and last update information.
4. Write Content for People and Machines
While Google recommends creating content for people only, entity-based SEO makes things a bit complex as you have to optimise content for both people and machines. However, the task becomes easy if you are using WordPress or Wix for content management.
-
Target Topics & Not Keywords: After the Panda update, creating separate content to target different variations of keywords is not viable. Instead, create in-depth articles that cover the whole topic where you can also target similar and long-tail keywords.
-
Fulfil the Search Intent: Put yourself in the searchers’ place and see what answers they are looking for. Do keyword research to find what stage of the funnel they are in and create targeted content that perfectly matches their search intent.
-
Write in Natural Language: Search engine bots have grown to understand natural languages and human talk to present accurate results for queries. Thus, write keeping the natural language of humans in mind.
Final Thoughts
Entities have become an essential part of modern-day SEO, providing users with the best possible results they are looking for. Now that you know the importance of entity optimisation, you can create better content that tailors your website to entity-based SEO.
Still need help? Our SEO agency in Sydney is well-versed in implementing strategic SEO requirements including entity SEO your business might have. We have a proven record of helping small to large enterprises achieve the desired results through organic means.
Contact us to consult with our team of expert SEO professionals for all your search engine optimisation needs.
DIGITAL MARKETING FOR ALL OF AUSTRALIA
- SEO AgencyMelbourne
- SEO AgencySydney
- SEO AgencyBrisbane
- SEO AgencyAdelaide
- SEO AgencyPerth
- SEO AgencyCanberra
- SEO AgencyHobart
- SEO AgencyDarwin
- SEO AgencyGold Coast
- We work with all businesses across Australia